Lesson 3: Data Structure - Arrays
Goals
- Introducing Arrays
- Declare & Initialise Arrays
- Access & Change Elements of an Array
- Looping Through Array Elements
- Pass and Return Arrays to/from Methods
- Code, code, code 🤩
Recap & Assignment check
Let’s look into the assignment from lesson 2
Arrays
An array is a collection of items. Each slot in the array can hold an object or a primitive value. Arrays can contain any type of element value (primitive types or objects), but you can’t store different types in a single array.
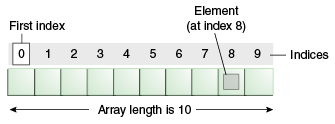
Each item in an array is called an element, and each element is accessed by its numerical index. As shown in the preceding illustration, numbering begins with 0. The 9th element, for example, would therefore be accessed at index 8.
Declare & Initialise Arrays
To create an array in Java, you use three steps:
- Declare a variable to hold the array.
- Create a new array object and assign it to the array variable.
- Store things in that array.
This is how you can declare arrays:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String names[]; //declaring string array called name
int[] numbers; // declaring an integer array called numbers
}
}
The second step is to create an array object and assign it to that variable. There are two ways to do this:
- Using
newkeyword - Directly initializing the contents of that array
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// using new keyword, declares an array of Strings and allocates memory for 10 Strings
String[] names = new String[10];
// declares an array of Strings, allocates memory for 4 Strings and initializes all elements
String[] definedNames = { "Alina", "James", "Anna","Johannes" };
}
}
Access & Change Elements of an Array
Once you have an array with initial values, you can get and change the values in each slot of that array. To get at a value stored within an array, use the array subscript expression ([]):
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] names = new String[10];
names[0] = "Alina";
System.out.println(names[0]);
names[0]= "Anna";
System.out.println(names[0]);
}
}
Looping Through Array Elements
In Java, we can also loop through each element of the array. Below example uses for loop to iterate through the array elements
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] names = new String[10];
for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
System.out.println(names[i]);
}
for (String name: names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
The property length is a built-in property to determine the size of any array. The following code prints the array’s size to standard output:
System.out.println(anArray.length);
Pass and Return Arrays to/from Methods
Pass an Array to Methods
Like variables, we can also pass arrays to methods. Where have you seen this before?
Return Array from Methods
A method can also return an array. For example, the below program returns an array from method incrementArrElements.
public static int[] incrementArrElements(int[] arr){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i]+=1;
}
// returning array
return arr;
}
Exercises and Assignments
Please click the link to download the assignment from GitHub Classroom.