Lesson 9: Data Structures - Set & Map
Goals
- What is a
Set? - When do I need a
Set? SetvsList- What is a
Map? - Understand the different types of
SetandMap.
Recap
- What is an
Array? - What is a
List? - What are the differences between
Array&List?
Presentation
What is a Set?
- A
Setis a collection of items that contains no duplicate items / only unique elements.
More formally, a
Setcontains no pair of itemse1ande2such thate1.equals(e2)is true.
- Let’s analyse the following code. What’s the final size of the
Set?public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); set.add(3); set.add(4); set.add(5); int size = set.size(); // ?? boolean contains3 = set.contains(3); // ?? boolean contains5 = set.contains(5); // ?? } } - Let’s analyse another code. What’s the final size of the
Set?public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); set.add(3); set.add(4); set.add(3); int size = set.size(); // ?? boolean contains3 = set.contains(3); // ?? boolean contains5 = set.contains(5); // ?? } }As stated above, you need a Set when you are interested in having only unique items.
What is a Map?
- A
Mapis a collection of unique keys and a corresponding (assigned) value for each key. - A
Mapallows you to look for a value based on a given key.
More formally, a
Mapis a collection of key-value pairs containing no pair of keysk1andk2such thatk1.equals(k2)is true.
- Let’s analyse the following code. What’s the final size of the
Map?public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("car", 5); map.put("bicycle", 2); map.put("bus", 0); int size = map.size(); // ?? boolean containsCar = map.containsKey("car"); // ?? boolean containsBus = map.containsKey("bus"); // ?? int car = map.get("car"); // ?? Integer bus = map.get("bus"); // ?? int bus = map.get("bus"); // ?? } }
As stated above, you need a
Mapwhen you are interested in keeping a dictionary or mapping of keys to values.
Useful methods of a Map
- put -> adds a key and value to the map
- get -> returns the value associated with the key
- containsKey -> returns if the key exists in the map
- remove -> removes the item with the given key from the map
Iterating over the elements of a Map
Different options:
By key:
for (String key: map.keySet()) {
int value = map.get(key);
System.out.println("The value associated to key " + key + " is " + value);
}
By EntrySet
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("The value associated to key " + entry.getKey() + " is " + entry.getValue());
}
Using own objects as keys for a map or entry of a set
If you want to use your own classes as keys for a map or element of a set you have to override the equals and the hashCode method of your new class.
Please review this explanation for more information.
HashSet and HashMap
- Ordering is not important
HashSetuses theequalsandhashCodemethods to ensure that the items in theSetare unique.HashMapuses theequalsandhashCodemethods to ensure that the keys in theMapare unique.
When in doubt, use the
HashSetandHashMap.
TreeSet and TreeMap
- Ordering is important
TreeSetis a Binary Search Tree that uses thecompareTomethod to ensure that the items in theSetare unique and are sorted in the right order.TreeMapis a Binary Search Tree that uses thecompareTomethod to ensure that the keys in theMapare unique and are sorted in the right order.- Learn about Binary Search Tree
Exercise
Remember the Star Classification challenge from the last assignment? Well, let’s implement it using a Map!
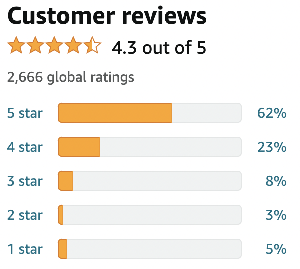
Define a class called Ratings, use a Map to store the ratings’ information, and implement all the following behaviours:
void addRating(int stars): Used for adding a rating from a customer. It receives a star rating from 0 to 5 (only).int getAmountRatings(): Returns the total amount of ratings given to this product.int getAmountRatings(int stars): Returns the total amount of ratings of a specific star (e.g. how many customers gave 4 stars for this product). The method should return 0 if an invalid rating is specified.float getAverageRating(): Returns the average of all given ratings for the product. If there are no ratings, it should return -1.